Finished projects
TAB-Scale 3: Das Haus das in die Zukunft blickt
Development of an innovative forecast-based control system for TAB
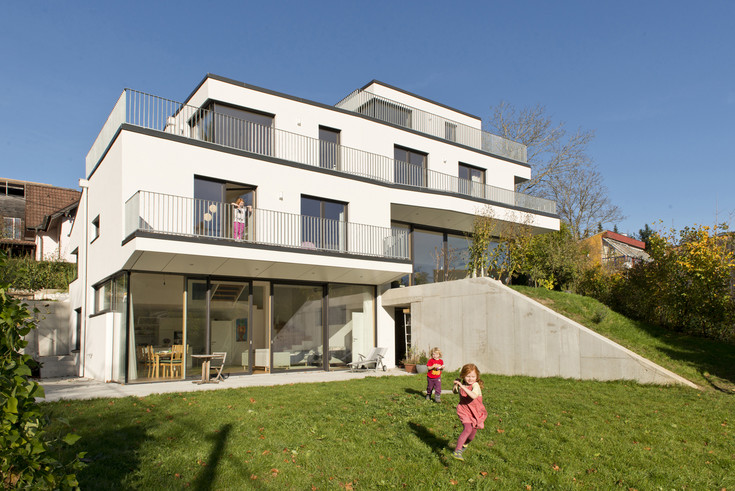
Residential buildings with thermal component activation are not building standard. In this research project, a residential building with thermal activated components is equipped with an innovative, modelpredictive control concept.
In the building, the positive effect of the high thermal storage capacity is used to minimize the heating energy demand. For this purpose, weather forecast data are processed and a room temperature curve for the future is predicted in a building model. An optimization algorithm is used to adapt the room temperature curve to a user setpoint and thus determine the necessary heating energy requirement.
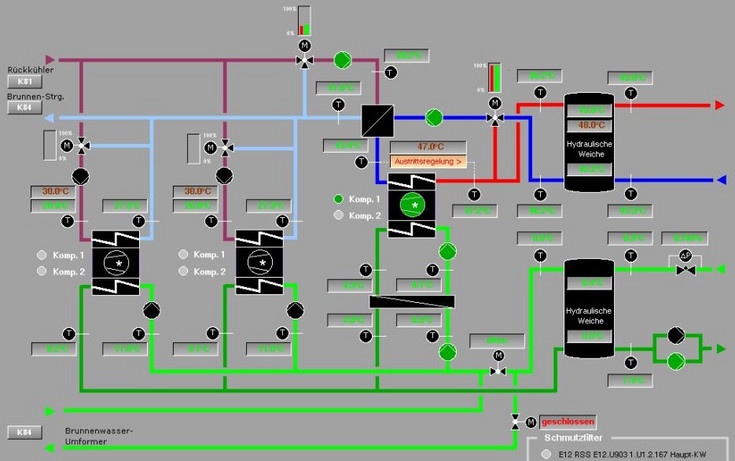
VICC - Virtual Cooling Control
Optimization of building refrigeration systems by integration of virtual data points into the building control system
In the course of this project, optimization measures for the control of refrigeration systems for building air conditioning are derived on the basis of simulation models that provide virtual data points.
The basis for the modeling are existing systems, which are measured and examined in detail. Different re-cooling systems and different sizes of refrigeration systems are selected for the investigation.
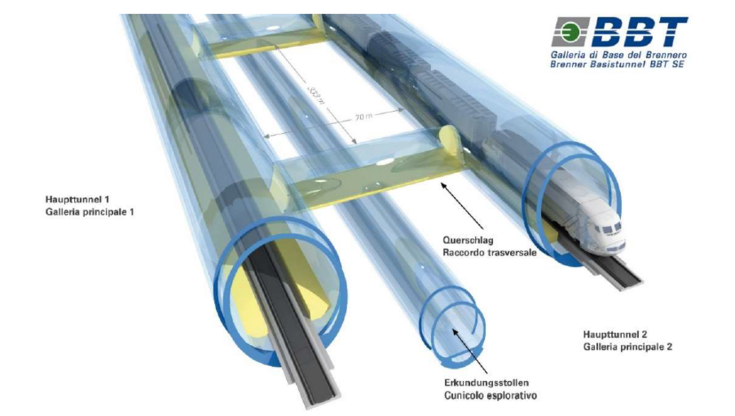
ThermoCluster
Survey of the thermal potential of large infrastructure projects for heat integration into urban energy grids
In this study, the thermal potentials of infrastructure objects as heat sources for urban systems are investigated.
The focus is on the Brenner Base Tunnel (BBT). The thermal heat source potential of the BBT is surveyed and an integration of the thermal energy into the district heating network of Innsbruck - in the form of an anergy or low-temperature district heating network - using heat pump systems is investigated.