Building technology
Refrigeration and heat pump systems play an important role in energy technology for heating and cooling.
Particularly in the field of building air conditioning and heating, these systems are an energy-efficient way of producing heat and cold with low energy input. But heat pumps can also make a key contribution to process heating and cooling. High-temperature heat pumps in particular can reduce CO2 emissions in the industry. Optimization potential can also be found in special refrigeration applications such as freeze drying.
At BOKU, research is being conducted on innovative refrigeration technology systems, but also on intelligent control concepts for these systems in the industrial, commercial and building field. Our team consists of DI Constanze Rzihacek, DI Thomas Keller, DI Bernhard Kling and DI Dr Magdalena Wolf. For questions and further information please contact DI Dr. Magdalena Wolf.
Current research initiatives and projects:
Refrigeration and heat pump technology, freeze drying, process simulation, exergy analysis, smart and innovative control systems
Sani60ies
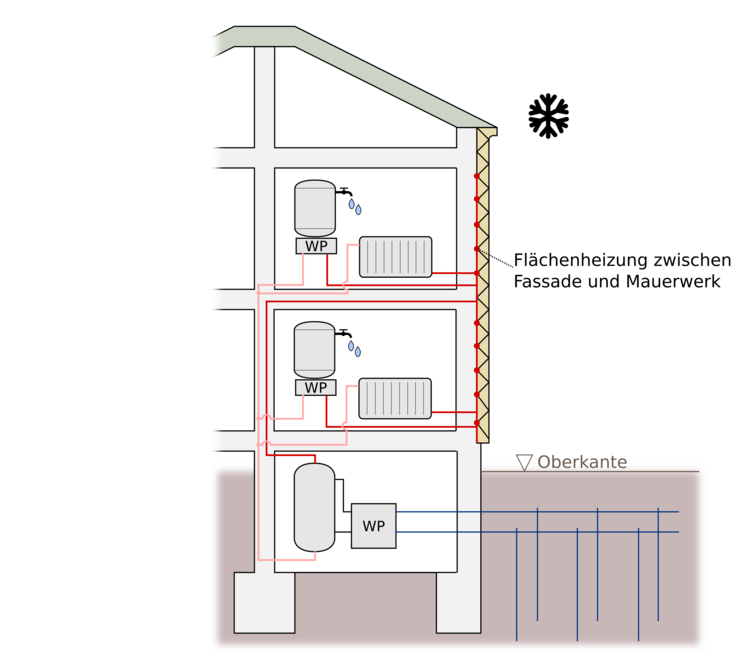
Demonstration of minimally invasive thermal and energy retrofits of classic 1950s - 60s apartment buildings
The project Sani60ies develops, tests and demonstrates a minimally invasive and socially acceptable refurbishment system with façade-integrated building component activation. The technology is being tested in "warm" refurbishments at two smaller properties before it is application in a 1960s housing development with over 200 apartments. The transferability of the system to the numerous building stock of unrenovated housing estates is the declared goal of the project.
ZQ3Demo

Implementation of urban future quarters with networking of actors and legal and economic replicable solutions
High proportions of highly volatile, renewable energy sources place great demands on our current energy system. The fundamental objective is that even with a high level of on-site energy generation, the public grids should not be burdened by additional peaks due to high feed-in (PV) or simultaneous consumption (e-cars, heating peaks)..
The aims of the project are to promote the replication of showcase neighbourhoods by demonstrating them in practice with accompanying research, monitoring and operational optimisation, as well as the further development of technical system solutions with regard to architecture, building energy systems and neighbourhood networking. A central element is the testing of an innovative, predictive control concept that regulates the heat input into the home not only according to comfort but also according to ecological and economic factors. To this end, 15 research flats were selected in the Campo Breitenlee future neighbourhood to be equipped with this special controller in order to test the effectiveness of the controller in practice.
Decarb Alt Erlaa
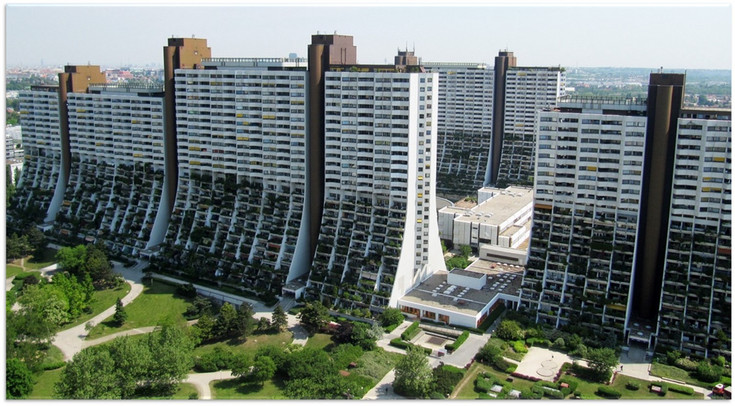

Decarbonisation of the Alt Erlaa residential park
The Alt Erlaa residential park, planned by architect Harry Glück in the 1970s and 1980s, is a beacon in the field of social housing. The aim of this project is to completely decarbonise the residential park with around 3,000 residential units and replace the currently installed gas boilers with heat pumps.
The project includes systematic analyses of potential with regard to structural measures, technical building measures and social science support for the transformation process. It also includes the feasibility analysis of innovative out-of-the-box technologies for CO2 binding during operation as well as a systematic risk analysis. With its considerable dimensions, it is suitable for initiating and implementing substantial technological and social innovations.
FlexHP
AI-supported control models for optimising the flexibility of heat pumps to reduce the load on the electricity grid
In the FlexHP project, a dynamic energy management system (DEMS) is being developed on a concept basis with the aim of developing an innovative and machine learning-supported control concept for heat pumps. At the heart of this DEMS are models of the various actors in the system and an algorithm that optimises the energy flows. One methodological focus is on modelling the actors in the energy system. Modern ICT technologies are used for this. The focus of the modelling is on the development of a reliable heat pump model for forecasting power consumption in combination with the thermal behaviour of the building. Finally, the individual models are combined in an overall forecast, which serves as the basis for controlling the energy flows. The function of the data management system is tested in a living lab.
SRI Demo

SRI Demo - Demonstration of smart technologies in buildings and support of the SRI test phase in Austria
In this research project, an Austrian method for assessing the SRI is being developed and evaluated. In addition, measures that contribute to an optimised SRI will be implemented using the example of 8 demonstration buildings. Based on
Based on the findings, an online platform for self-testing of buildings by stakeholders will be developed, a practicable methodology for Austria will be found, and the SRI platform at EU level and its structure and activities will be co-designed.
UKÖ - Urbaner Kältebedarf Österreich

Urban cooling demand in Austria 2030/2050
In this project, the Austrian demand for cooling over the next 25 years is estimated and graphically visualised using GIS-based methods. The project is supplemented by an intensive technology analysis of measures to reduce indoor temperatures and a feasibility study based on 5 selected urban neighbourhoods in Austria.
Optimization of refrigeration systems for freeze drying
Optimized plant dimensioning of freeze dryers refrigeration system based on process simulation
Freeze-drying processes are widely used in food and biotechnology. Freeze drying systems must be able to generate temperatures down to -80°C and vacuum down to 0.001 mbar.
These high requirements can also be applied to the refrigeration technology used in freeze dryer. In practice, plant planning and design is primarily based on empirical valuee. Technical guidelines and standards are lacking.
In a research cooperation with a company from the freeze drying sector, simulation-based calculation models are being developed in order to provide a technically sound process dimensioning.
Alpenland Zukunftshaus Wolkersdorf
Hygienically safe domestic hot water production with cascaded heat pumps and innovative, forecast-based controller for TAB
An innovative multi-storey residential building with thermal activated components is equipped with a hygienically safe cascaded water heating system and a model predictive control concept.
In the research project, different, cascaded water heating methods will be techno-economically investigated and evaluated. The most efficient system will be implemented in the planned residential building. In addition, an innovative control concept based on weather forecast data will be implemented for optimized heating and cooling operation.
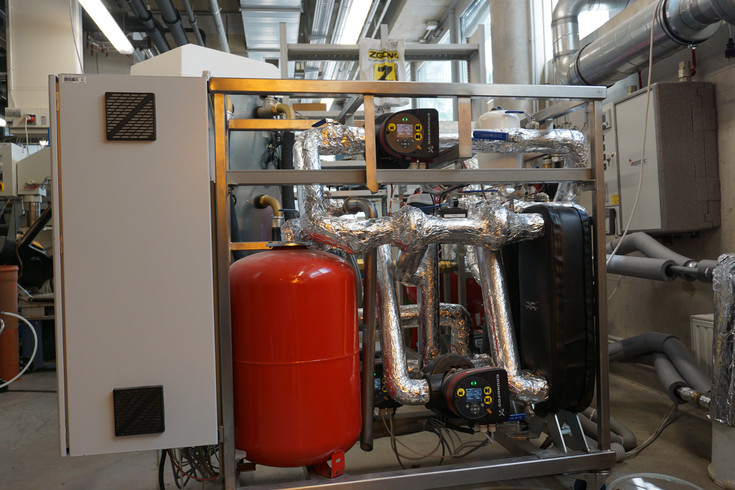
High temperature heat pump testing station
Efficiency verification of high temperature heat pumps
To measure high temperature heat pump systems, a good infrastructure is very important because high temperature and pressure levels of the high temperature heat pump system requires special demand for the testing station. The hole system is designed for nominal pressures up to 25 bar and maximum temperatures of 200°C and covers a power range from 15 to 50 kW.
The testing bench runs with an energy efficient recycling heat system and allows individual adjustable temperature levels in the heat circle. With comprehensive measurement techniques, the detection of relevant parameters for scientific research is possible and allows the calculation of major energy operating numbers.

![[Translate to English:] DI Dr. Magdalena Wolf © Kamiki](/fileadmin/_processed_/6/d/csm_foto2_bewerbungsfoto_45x60mm_v3_e3696e968f.jpg)