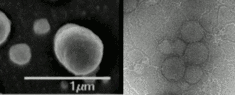
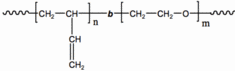Amphiphilic di-block copolymers such as poly(butadiene)-poly(ethylene oxide) comprise a hydrophobic and a hydrophilic domain. This property allows the molecule to self-assemble into a variety of structures when in contact with either organic or aqueous solvents.
Polymers with different ratios of hydrophic to hydrophilic content are commercially available. By selecting polymers of the appropriate ratio, artificial bilyared membranes can be synthesised in the form of sheets or vesicles.
In addition to the advantages inherent in artificial phospholipid membranes, polymeric membranes offer greater stability over time, relative ease of production as well as finer control over chemistry and amphiphilicity.