Refrigeration technology, heat pump systems and smart controlling
Wärmepumpen und kältetechnische Anlagen spielen zum effizienten Heizen und Kühlen in der Gebäude- und der Energietechnik allgemein - eine bedeutende Rolle. Vor allem in der Gebäudetechnik sind diese Systeme eine energieeffiziente Möglichkeit, Wärme und Kälte mit geringem Energieaufwand zu erzeugen. Aber auch in der Prozesswärme und -kühlung können Wärmepumpen einen wichtigen Beitrag leisten. Vor allem Hochtemperatur-Wärmepumpen können den CO2-Ausstoß in der Industrie reduzieren. Optimierungspotenzial gibt es auch bei speziellen Kälteanwendungen wie der Gefriertrocknung.
An der BOKU wird an innovativen kältetechnischen Anlagen, aber auch an intelligenten Regelungskonzepten für diese Anlagen im Industrie-, Gewerbe- und Gebäudebereich geforscht. Unser Team besteht aus DI Constanze Rzihacek, DI Thomas Keller, DI Bernhard Kling und DI Dr. Magdalena Wolf. Für Fragen und weitere Informationen kontaktieren Sie bitte DI Dr. Magdalena Wolf.
Aktuelle Forschungsschwerpunkte und Projekte:
Anwendung von Wärmepumpen und kältetechnischen Anlagen in der Gebäudetechnik und der Industrie, kältetechnische Anwendungen im Zusammenhang mit Gefriertrocknung, Prozesssimulation und dynamische Gebäudesimulation, Exergie Analysen, smarte und innovative Regelungsstrategien für die Gebäudetechnik
Sani60ies
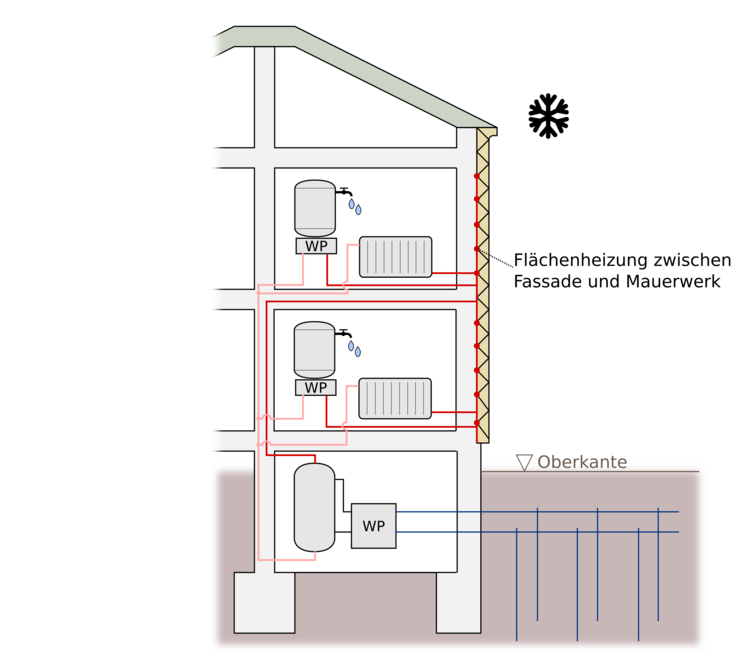
Demonstration minimal invasiver thermischer und energetischer Sanierung klassischer Wohnhausanlagen der 1950 - 60er Jahre
Das Projekt Sani60ies entwickelt, testet und demonstriert ein minimalinvasives und sozialverträgliches Sanierungssystem mittels fassadenintegrierter Bauteilaktivierung. Die Technologie wird in 3 Demonstrationsobjekten getest und demonstriert. Dabei steht auch die Entwärmung in den Sommermontaten im Fokus. Erklärtes Ziel ist die Übertragbarkeit des Systems auf einen Großteil des unsanierten Gebäudebestands dieser Bauperiode vor allem in urbanen Regionen.
ZQ3Demo

Umsetzung von urbanen ZukunftsQuartieren mit Akteursvernetzung und rechtlich‐ökonomisch replizierbaren Lösungen
Hohe Anteile stark volatiler, erneuerbarer Energiequellen stellen große Anforderungen an unser heutiges Energiesystem. Als grundsätzliches Ziel gilt dabei: Auch bei einer hohen Vor-Ort Energieaufbringung sollen die öffentlichen Netze möglichst nicht durch zusätzliche Spitzen auf Grund von hoher Einspeisung (PV) oder gleichzeitigem Verbrauch (E-Autos, Heizungsspitzen) belastet werden.
Ziele des Projekts sind einerseits die Förderung der Replikation von Vorzeigequartieren durch die Demonstration in der Praxis mit begleitender Forschung, Monitoring und Betriebsoptimierung, sowie andererseits auch die Weiterentwicklung von technischen Systemlösungen hinsichtlich Architektur, Gebäudeenergiesysteme und Quartiersvernetzung. Ein zentrales Element ist die Erprobung eines innovativen, prädiktiven Regelungskonzepts, dass den Wärmeeintrag in die Wohnung nicht nur nach Komfort sondern auch nach ökologischen und ökonomischen Faktoren regelt. Dafür wurden im Zukunftsquartier Campo Breitenlee 15 Forschungswohnungen ausgewählt, die mit diesem speziellen Regler ausgestattet werden, um die Effektivität des Reglers in der Praxis zu testen.
Decarb Alt Erlaa
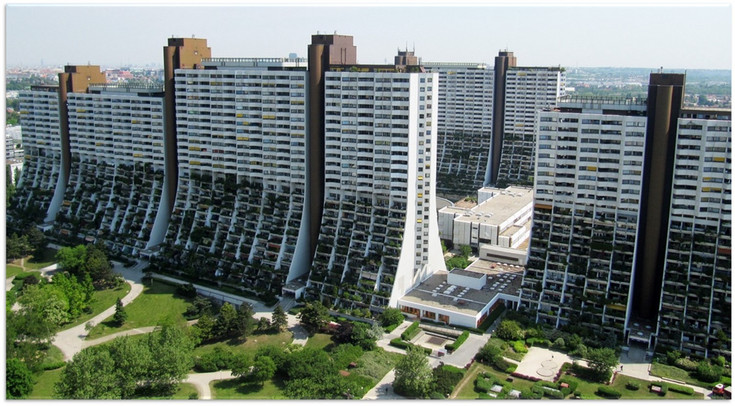

Decarbonisierung des Wohnparks Alt Erla
Der Wohnpark Alt Erlaa, vom Architekten Harry Glück in den 1970er und 1980er Jahren geplant, ist ein Leuchtturm im Bereich des sozialen Wohnbaus. Ziel dieses Projekts ist es, den Wohnpark mit ca. 3000 Wohneinheiten vollständig zu decarbonisieren und die derzeit installierten Gaskessel durch Wärmepumpen zu ersetzen.
Das Projekt beinhaltet systematische Potenzialanalysen hinsichtlich bautechnischer Maßnahmen, hinsichtlich gebäudetechnischer Maßnahmen und hinsichtlich einer sozialwissenschaftlichen Begleitung des Transformationsprozesses. Es beinhaltet außerdem die Machbarkeitsanalyse innovativer out of the box - Technologien zur CO2 Bindung im Betrieb sowie eine systematische Risikoanalyse. Mit seiner beachtlichen Dimension ist es geeignet, substanzielle technologische und soziale Innovationen anzustoßen und umzusetzen.
FlexHP
KI-gestützte Reglungsmodelle für die Flexibilitätsoptimierung von Wärmepumpen zur Entlastung des Stromnetzes
Im Projekt FlexHP wird ein dynamisches Energiemanagementsystem (DEMS) auf Konzeptbasis entwickelt, das auf ein innovatives und Machine Learning-gestütztes Regelungkonzept für Wärmepumpen abzielt. Kern dieses DEMS sind Modelle der verschiedenen Akteure im System sowie ein Algorithmus, der die Energieströme optimiert. Ein methodischer Schwerpunkt liegt auf der Modellierung der Akteure im Energiesystem. Dabei kommen moderne Technologien der IKT zur Anwendung. Fokus der Modellierung liegt in der Entwicklung eines belastbaren Wärmepumpenmodells zur Prognose des Leistungsverbrauchs in Kombination mit dem thermischen Verhalten des Gebäudes. Abschließend werden die einzelnen Modelle in einem Gesamt-Forecast verschränkt, der als Basis für die Regelung der Energieströme dient. Die Funktion des Datenmanagementsystem wird in einem Living Lab erprobt.
SRI Demo

SRI Demo - Demonstration intelligenter Technologien in Gebäuden und Unterstützung der SRI-Testphase in Österreich
In diesem Forschungsprojekt wird eine österreichische Methode zur Bewertung des SRI entwickelt und evaluiert. Zudem werden am Beispiel von 8 Demonstrationsgebäuden Maßnahmen umgesetzt, die zu einem optimierten SRI beitragen. Auf
Basis der Erkenntnisse soll eine Onlineplattform zum Selbst-Testen von Gebäuden durch Stakeholder entwickelt, eine für Österreich praktikable Methodik gefunden, und die SRI Plattform auf EU-Ebene sowie deren Struktur und Aktivitäten mitgestaltet werden.
UKÖ - Urbaner Kältebedarf Österreich

Urbaner Kältebedarf in Österreich 2030/2050
In diesem Projekt wird der österreichische Kältebedarf in den kommenden 25 Jahren abgeschätzt und mittels GIS-basierten Methoden graphisch dargestellt. Ergänzt wird das Projekt durch eine intensive Technologieanalyse von Maßnahmen zur Reduktion der Innenraumtemperatur und eine Machbarkeitsstudie anhand von 5 ausgewählten Stadtquartieren in Österreich.
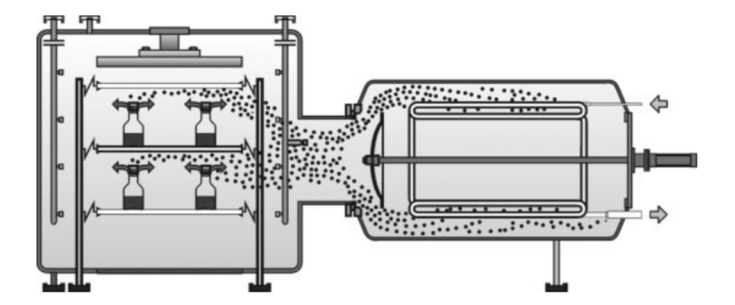
Optimization of refrigeration systems for freeze drying
Optimized plant dimensioning of freeze dryers refrigeration system based on process simulation
Freeze-drying processes are widely used in food and biotechnology. Freeze drying systems must be able to generate temperatures down to -80°C and vacuum down to 0.001 mbar.
These high requirements can also be applied to the refrigeration technology used in freeze dryer. In practice, plant planning and design is primarily based on empirical valuee. Technical guidelines and standards are lacking.
In a research cooperation with a company from the freeze drying sector, simulation-based calculation models are being developed in order to provide a technically sound process dimensioning.
Alpenland Zukunftshaus Wolkersdorf
Hygienisch sichere Warmwasserbereitung mit kaskadierten Wärmepumpen und innovativem, prognosebasiertem Regler für TAB
Ein innovativer mehrgeschossiger Wohnbau mit thermisch aktivierten Bauteilen wird mit einer hygienisch sicheren kaskadierten Warmwasserbereitung und einem modellprädiktiven Regelungskonzept ausgestattet.
In dem Forschungsprojekt werden verschiedene, kaskadierte Wassererwärmungsverfahren technisch-wirtschaftlich untersucht und bewertet. Das effizienteste System wird in dem geplanten Wohngebäude umgesetzt. Darüber hinaus wird ein innovatives Regelungskonzept auf Basis von Wettervorhersagedaten für einen optimierten Heiz- und Kühlbetrieb implementiert.
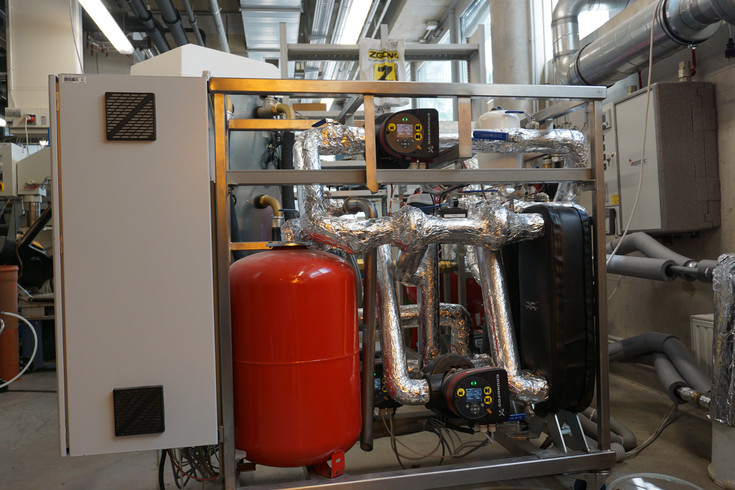
High temperature heat pump testing station
Efficiency verification of high temperature heat pumps
To measure high temperature heat pump systems, a good infrastructure is very important because high temperature and pressure levels of the high temperature heat pump system requires special demand for the testing station. The hole system is designed for nominal pressures up to 25 bar and maximum temperatures of 200°C and covers a power range from 15 to 50 kW.
The testing bench runs with an energy efficient recycling heat system and allows individual adjustable temperature levels in the heat circle. With comprehensive measurement techniques, the detection of relevant parameters for scientific research is possible and allows the calculation of major energy operating numbers.