XR-BEM: Real-time Interactive Building Simulation in Extended Reality Based on the Generalizable Surrogate Model
SUPERVISOR: Benjamin KROMOSER
PROJECT ASSIGNED TO: Zishu LUO
With the global push for carbon neutrality and the rising demand for indoor comfort, modern building systems are becoming increasingly complex. To describe them accurately, building energy models (BEMs) have also become
more sophisticated. As a result, their inputs, outputs, and the relationships between them have evolved to be more high-dimensional and interdependent. However, traditional energy analysis depends largely on static reports and two-dimensional charts. Such presentation methods often hinder a clear understanding of complex BEMs that involve numerous parameters and intricate input–output relationships. Meanwhile, static 2D representation restricts users from actively exploring data or considering alternative perspectives, leaving stakeholders as passive recipients of predetermined information. Because of stakeholders’ diverse backgrounds, they often interpret BEM information unevenly, and this divergence affects the optimization of design solutions while weakening collaborative decision-making in projects. Alternatively, Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR), collectively referred to as Extended Reality (XR), provide immersive 3D visualization and intuitive interaction capabilities, making them well-suited for translating complex BEM data into interactive and user-friendly platforms.
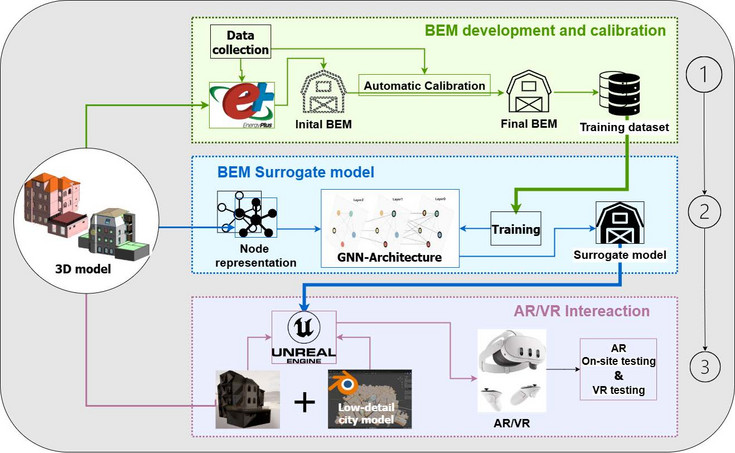
This research aims to develop a novel BEMs system with real-time interactivity based on XR, hereafter referred to as XR–BEM, which is designed to overcome the static limitations of traditional building energy simulation in
both workflow and result representation. Delivering such an XR–BEM system, however, will require more than advanced visualization. At its core, the system needs a high-fidelity, rigorously calibrated white-box BEM to ensure that the interactive results are both accurate and reliable. Yet, current white-box simulation tools often take considerable time to compute for complex BEM, making real-time interaction impractical. To address this limitation, the use of surrogate models offers a promising solution, enabling rapid responses while maintaining acceptable accuracy.
Based on these considerations, this research proposes a three-phase modular approach, where each module builds on the previous one to implement the system progressively. The first phase will focus on developing a standardized automatic calibration workflow to enhance BEM accuracy and data quality. Building on this foundation, calibrated BEM will then be used to generate data for training an initial rapid-response surrogate model based on Graph Neural Networks. Finally, the surrogate model will be integrated into XR environments to implement an interactive visualization prototype application, thus effectively replicating the predictive accuracy of the original high-quality BEM while drastically reducing computational cost, which enables real-time interaction. The research integrates the capabilities of XR technology in visualization and interaction with surrogate model real-time feedback, leveraging the strengths of BEM calibration in simulation accuracy and physical interpretability. In doing so, it will transform passive 2D traditional static energy analysis and data presentation into dynamic 3D interactive exploration, and is further expected to support a wide range of users, from energy modelers and architects to facility managers and end users, enabling cross-phase and cross-role collaborative decisionmaking throughout the entire building life cycle. This system introduces an innovative approach that will enhance the scientific rigor and efficiency of data-driven decision-making in both new construction and deep renovation projects, thereby providing strong support for the digital and intelligent transformation of the architecture, engineering, and construction (AEC) industry.
Keywords—BEM, Calibration, Surrogate model, Machine learning, GNN, XR, Real-time interaction, Unreal engine