Neue Publikation – Fernandes et al. 2026
Resilience-Oriented Extension of the RAMSSHEEP Framework to Address Natural Hazards Through Nature-Based Solutions: Insights from an Alpine Infrastructure Study
Sérgio Fernandes, Erik Kuschel, Michael Obriejetan, Rosemarie Stangl, Johannes Hübl, Florentina D. Ionescu, Agnieszka Bigaj-van Vliet, José Matos and Alfred Strauss
22 January 2026
https://doi.org/10.3390/infrastructures11010035
Abstract
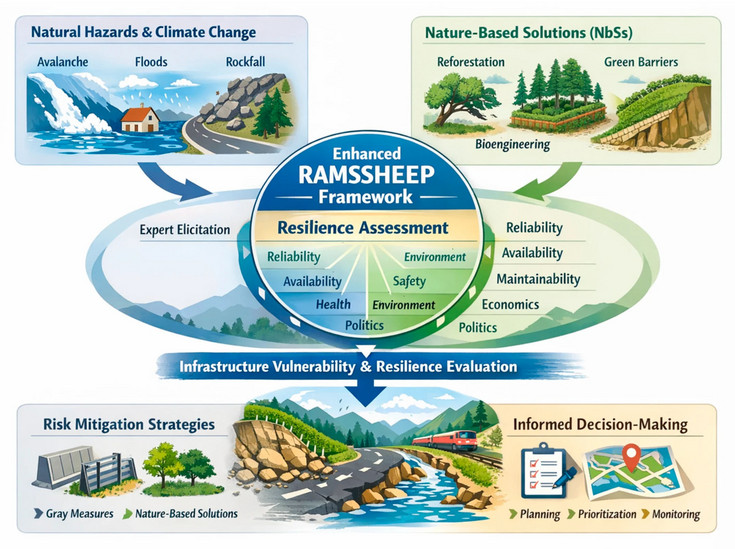
Climate change is increasing the frequency and intensity of natural hazards, placing additional stress on critical infrastructure systems. Addressing these challenges requires both robust evaluation frameworks and the inclusion of Nature-Based Solutions (NbSs) alongside conventional protection measures. Building on the RAMSSHEEP concept, originally proposed for risk-driven maintenance, and later further developed and applied in, e.g., previous Horizon projects and COST Action TU1406, this study integrates natural hazard considerations and NbS risk mitigation measures into a comprehensive approach to evaluate the resilience of critical infrastructure. The novel methodology involves a structured expert elicitation process with participants from the Horizon NATURE-DEMO project, to adapt and extend the RAMSSHEEP framework for resilience-oriented transformation. This also includes alignment with established hazard and risk assessment systems to ensure methodological consistency and applicability of the final concept. The resulting framework enables systematic evaluation of infrastructure vulnerability and resilience, explicitly accounting for natural hazards and the contribution of NbSs to risk mitigation. The expected outcome is an objective, repeatable assessment methodology that supports decision-makers in planning, prioritizing, and monitoring resilience-enhancing measures across the infrastructure life cycle. A particular focus of this contribution lies in the methodological approach, ensuring its applicability within interdisciplinary and multi-level decision-making contexts.
Keywords: critical infrastructure resilience; natural hazards; climate change adaptation; Nature-based Solutions (NbSs); RAMSSHEEP framework; expert elicitation; risk assessment and management